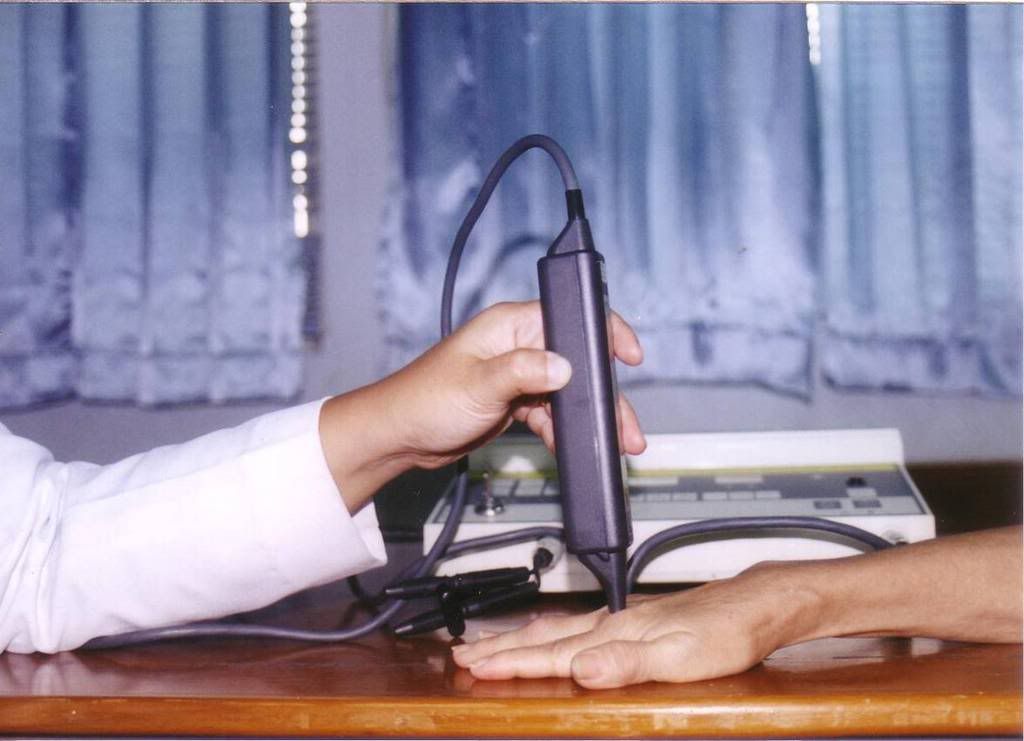
A friend of mine, a dentist, came to me, numbness on her right hand as the chief complaint. That is a very specific injury to whom who uses hand, especially the wrist, rhythmic and for a long time. It usually occurs in people who work as a dentist (like my friend), somebody who works a lot using computer, or in Indonesia, during fasting month, housewives suffer from Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) due to their repeated work of making “sambal” using “cobek”. Apparently, CTS is one of ladies’ disease.


Pathogenesis:
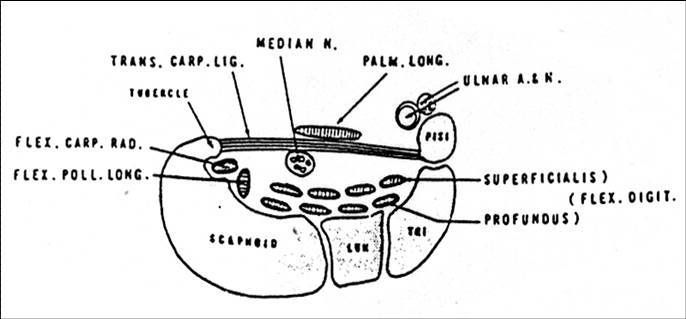
CTS is caused by impingment of the median nerve inside the carpal tunnel. As tension inside the tunnel increases, perineural edema occurs, and causes damage to the nerve. This event will release serotonin and prostaglandin, and impair microcirculation. This is the mechanism which stimulate the pain.
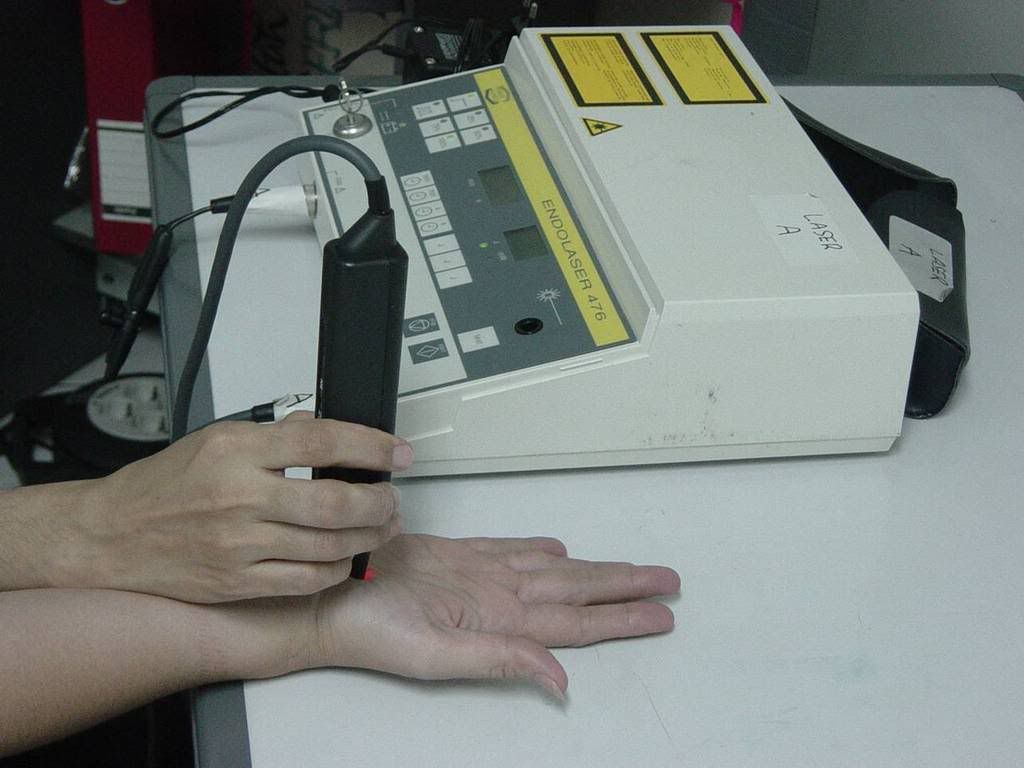
Laser therapy:
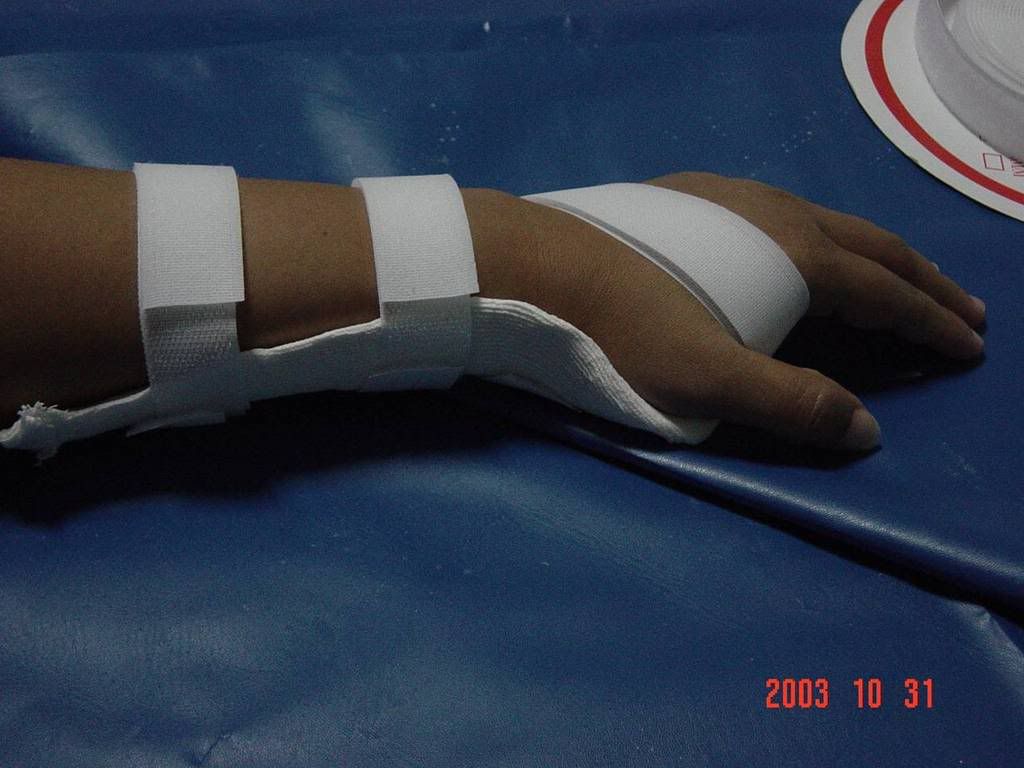
I gave her diode laser (15 mW for 15 minutes) with trans-cutaneous application. The day after her first visit, she told me that after the treatment she felt an “uncomfortable sensation” in her injured hand. I decided to decrease the dosage of laser therapy to 10mW for 15 minutes. She felt comfortable with this regiment and could work as usual. Orthose also given to fixate the wrist at zero degree position.
Research
A research on CTS has been conducted at the Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Department in
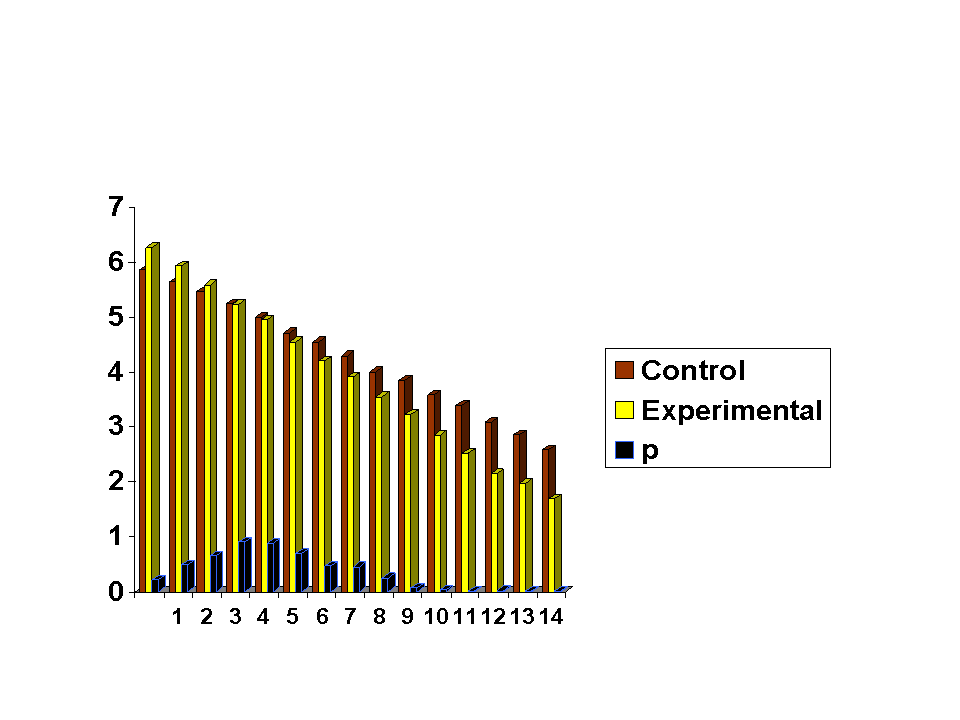
There were two groups, LLLT combined with plaster of Paris, and the other as control only using plaster of Paris.
The subjects were homogenous among those groups. It was conducted for a period of two weeks, and Visual Analog Scale (VAS) was used as outcome assessment for pain.
Conclusion: Application of plaster of Paris and Low Level Laser Therapy has an additional effect for pain reduction in comparison to plaster of Paris only
Discussion:
The effect of Low Level Laser Therapy as anti inflammatory and pain reliever worked in this case of CTS.
Acknowledgement:
This story is dedicated to Mrs. Hermina., a friend of mine who is such a beautiful dentist.
(Hi, Mrs Hermina, , your visit to my office reminded me to share this kind of problem to others. Thank you)